Biology: Chapter 6: DNA and Nucleic acids: DNA replication
- In 1953, James and Watson Crick used the results of work by Rosalin Franklin to develop a model of the structure of DNA.
- Semi-conservative replication: Method of copying where half of the original molecules are kept (conserved) in the new molecules.
Simple diagram of semi-conservative replication in DNA.
- Enzyme Helicase unzips parental double helix, separating the two strands.
- Replication fork: Where the DNA strands are separating.
Replication fork.
- Single-strand binding proteins: Keep the two parental strands separated by temporarily hydrogen bonding to the bases.
- Primase: Adds RNA primer to DNA strand
- RNA primer: Initiate DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase
- DNA polymerase: Builds a new strand by assembling the nucleotides to the parental strand. Nucleotide bases form the specific bonds with its complementary base on the parental strand, therefore it is almost impossible to make a mistake. Only works in a 5' to 3' direction.
- Since DNA polymerase can only work from a 5' to 3' direction, one strand can be built continuously as the replication fork progresses.
- Leading strand: Strand that is built continuously from from 5' to 3'.
- However, one strand will have the replication fork progressing towards 5'. This strand will grow in the overall direction of 5' to 3' by the addition of short fragments as the replication fork progresses.
- Lagging strand: 3' to 5' strand that needs to be built in fragments.
- Okazaki fragments: Fragments used to build the 3' to 5' strand.
- Another DNA polymerase replaces RNA primer with DNA.
- DNA ligase: Joins okazaki fragments together to growing strand.
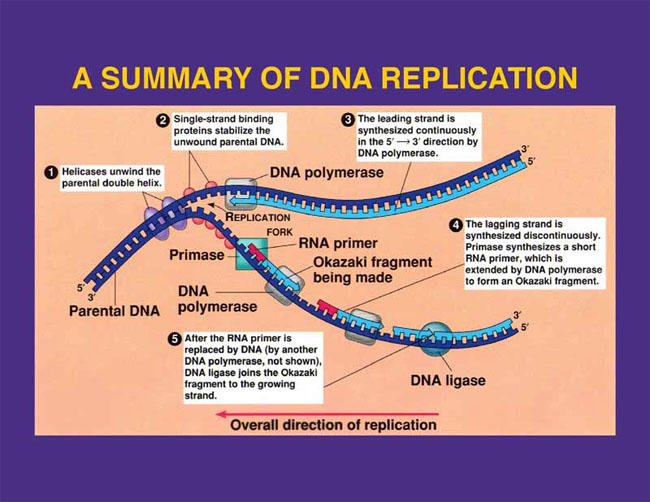
DNA replication diagram.
Proofreading DNA
- DNA polymerase proofreads each nucleotide and removes incorrectly paired nucleotides.
Repairing DNA
- DNA molecules that are exposed to harmful chemical and physical agents eg. Tobacco, UV rays can change nucleotides, which can affect encoded genetic information. However, the DNA has some ways of fixing it.
Nucleotide excision repair:
- Nuclease enzyme: Cuts damaged DNA strand at it's 2 points.
- Repair synthesis by DNA polymerase fills gap
- DNA ligase: Seals the phosphate sugar backbone together.
No comments:
Post a Comment