Biology: Chapter 6: Nucleic acids and protein synthesis: DNA and RNA structure
Nucleotides aka Nucleic acids
- Smaller molecules that DNA and RNA are made up of.
- Polynucleotides: Long chains of nucleotides eg. DNA and RNA.
- Composed of 3 components:
-Pentose sugar
-Nitrogen-containing base
-Phosphate group
 Structure of nucleotide.
Structure of nucleotide.- Pentose sugar: Sugar with 5 carbons. Can be either Ribose (in RNA) or Deoxyribose (in DNA.
- Deoxyribose: Missing an oxygen on it's second carbon primer.
Nitrogen-containing bases aka Nitrogenous bases
- Purine bases: Double ring structure - Adenine, Guanine.
- Pyrimidine bases: Single ring structure - Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil.
- DNA contains the 4 bases A-T and C-G, but never Uracil.
- RNA contains the 4 bases A-U and C-G, but no Thymine.
 Structural formulae of the nitrogenous bases.
Structural formulae of the nitrogenous bases.
ATP: Similar structure to a nucleotide. Adenosine (Ribose sugar with the base Adenine) can be combined to 1,2 or 3 phosphates to make Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP), Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) or Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
Polynucleotides
- Polynucleotide: Many nucleotides linked together in a chain.
- Formed during interphase of the cell cycle.
- Sugar-phosphate backbone: Alternating sugars and phosphates of the nucleotides linked together with the bases projecting sideways.
- Phosphodiester bonds: Covalent sugar-phosphate bonds.
- Phosphodiester bonds link the Carbon 5 of one sugar to the Carbon 3 of the next.
- The polynucleotide is said to have 3' and 5' ends: the end where the Carbon 3 has nothing to link is called the 3' end, while the end where the Carbon 5 has nothing to link to is called the 5' end.
- Bases can be purines or pyrimidines: Purines only link with pyrimidines, but it is even more precise.
- In a DNA molecule, there is only enough room between the two sugar-phosphate backbones for 1 purine and 1 pyrimidine molecule, so a pyrimidine can only bond with a purine, since purines are larger.
- Adenine and Thymine form double hydrogen bonds, whereas Guanine and Cytosine form a triple hydrogen bond, therefore only pairs possible are A-T and C-G.
- Complementary base pairing: The precise pairing of bases due to hydrogen bond and structure size (purine/pyrimidine) : Adenine and Thymine (A-T), and Cytosine and Guanine (C-G).
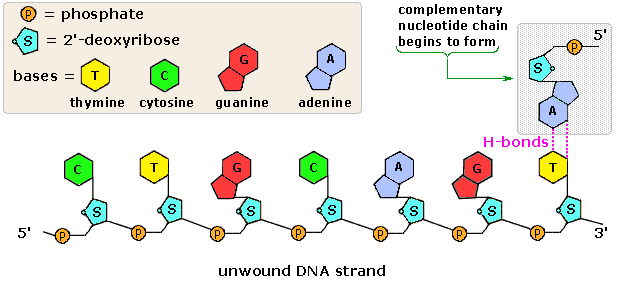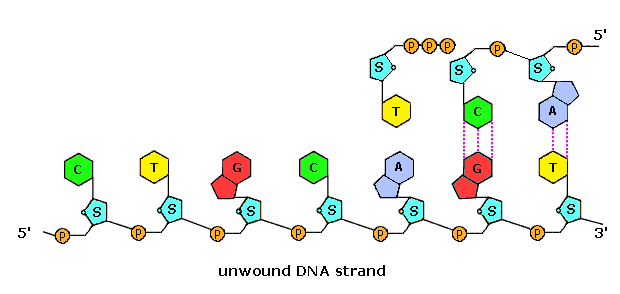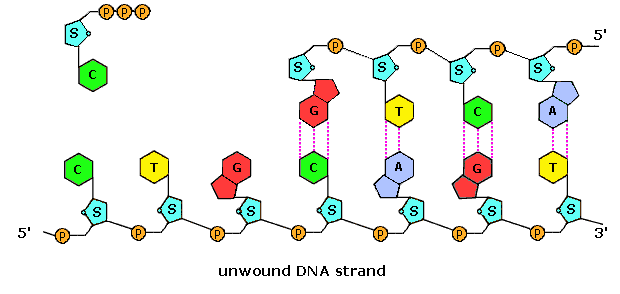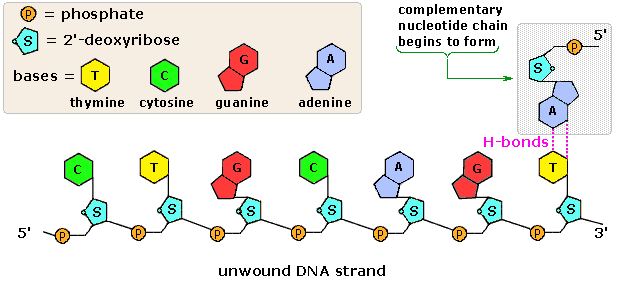 Animation of DNA replication and the DNA strand.
Animation of DNA replication and the DNA strand.- Double helix: Two strands wrapping around each other - the 3D shape DNA molecules form.
- Hydrogen bonds linking the bases easily broken, which happens during DNA replication and protein synthesis.
- RNA molecules are only single stranded.
Creative Peptides is specialized in the process development and the manufacturing of bioactive peptides. Neoantigen Peptides Vaccine
ReplyDelete